Vibration #1: Modal
Analysis of a Turbine
Introduction:
In the
area of dynamics and vibrations the natural frequencies of a structure
is of great importance to determine whether a structure can withstand
excitation from the surroundings. In this example, we will learn to
model a turbine and then determine its first few natural frequencies.
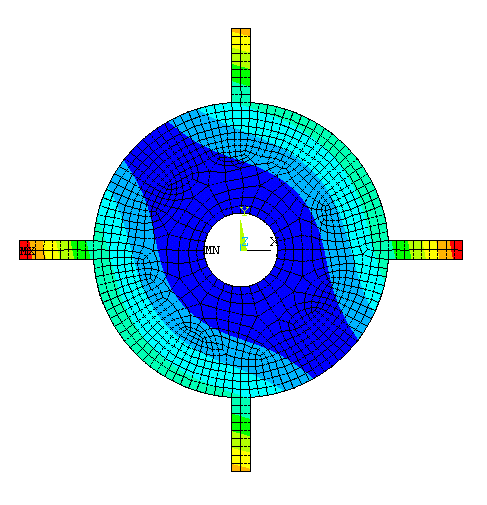
Physical Problem: To
determine the natural frequencies of the turbine shown in the figure.
Modal analysis means the calculation of the natural frequencies of a
mechanical system. It also involves the calculation of the mode shapes.
Problem Description:
 |
We will model the
turbine as a disk with blades fixed on it ('blisk'=bladed
disk). The inner radius of the hub is 10 cm, outer radius is 40 cm,
blade length is 20 cm, blade width is 5 cm, and the thickness is 2.5
mm |
 |
Material:
Assume the structure is made of steel with modulus of elasticity E=210
GPa and has a
Poisson ratio of 0.3 and density of 7.21e3 kg/cubic meter. |
 |
Boundary conditions:
The blisk is fixed around the inner
diameter of the disk. |
 |
Loading:
The blisk is not loaded. |
 |
Objective:
 |
To determine
first three family of modes. |
 |
To animate the
mode shape of the first 3 modes. |
 |
You are required
to hand in print outs for the above. You don't have to hand in the
animation files but you will have to give at least 3 captured frames
of the animation for each of the three modes. |
|
 |
Figure:
|
STARTING ANSYS:
 |
Click on ANSYS
6.1 in the programs menu. |
 |
Select
Interactive. |
 |
The following menu
that comes up. Enter the working directory. All your files will be
stored in this directory. Also enter 64 for Total Workspace and
32 for Database. |
 |
Click on Run.
|
MODELING
THE STRUCTURE:
 |
We will model one
quarter of the blisk and then reflect it
to create the complete blisk.3 |
 |
Go to the ANSYS
Utility Menu.
 |
Click
Workplane>WP
Settings.
|
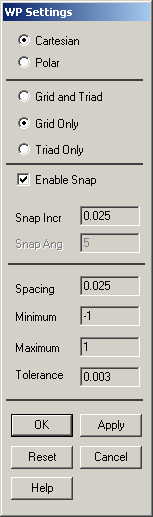
 |
The following
window comes up: |
|
 |
Check the Cartesian
and Grid Only buttons |
 |
Enter the values
shown in the figure above. |
 |
The following is
the quarter blisk we will model first:
|
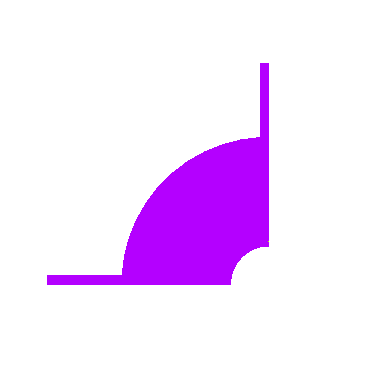
 |
Go to the ANSYS
Main Menu
Preprocessor>Modeling>Create>Areas>Rectangle>By 2 corners.
|
 |
Select the two
corners for the horizontal rectangle and click Apply. Remember the
rectangles (blades) have a thickness half the actual thickness since
we are modeling only a quarter of the blisk.
|
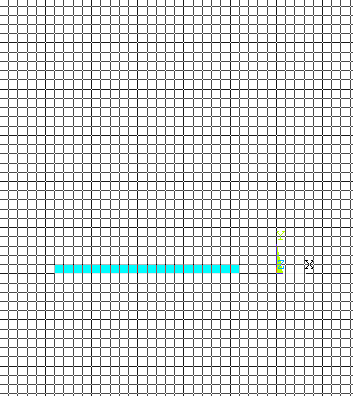
 |
Now similarly
create the vertical rectangle. |
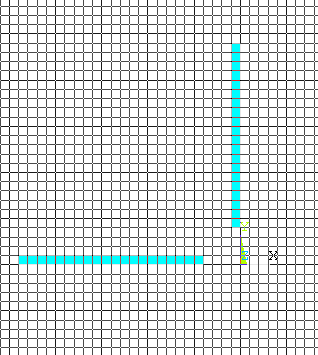
 |
Now we will create
the quarter disk. Go to
Preprocessor>Modeling>Create>Areas>Circle>Partial Annulus.
The following window comes up: |
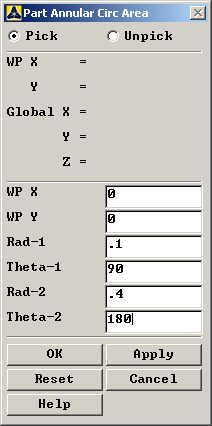
 |
Enter the values as
shown and click OK. The model looks like the one below: |
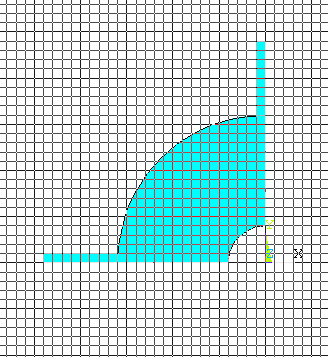
 |
Now we will reflect
the areas we have created about the YZ plane and then all the areas
about the XZ plane. Go to
Preprocessor>Modeling>Reflect>Areas.
Click on "Pick All". the following window comes up:
|
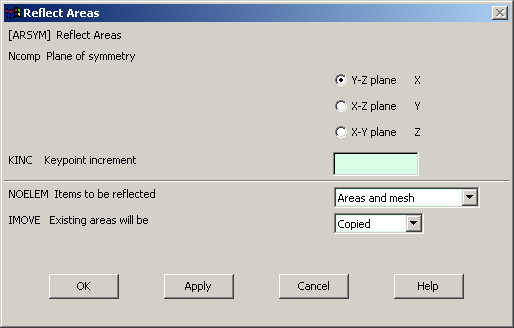
 |
Select the YZ plane
and say OK. The figure will look like the following: |
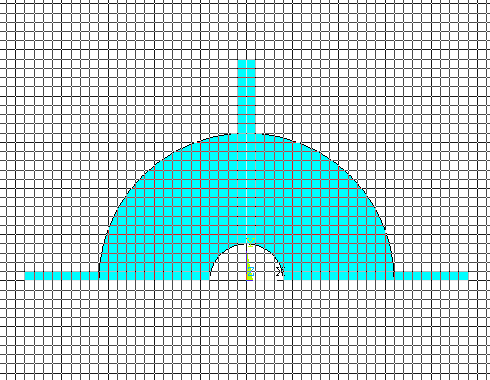
 |
Now repeat the same
process and reflect the whole figure about the XZ plane. The figure
will look like this now. |
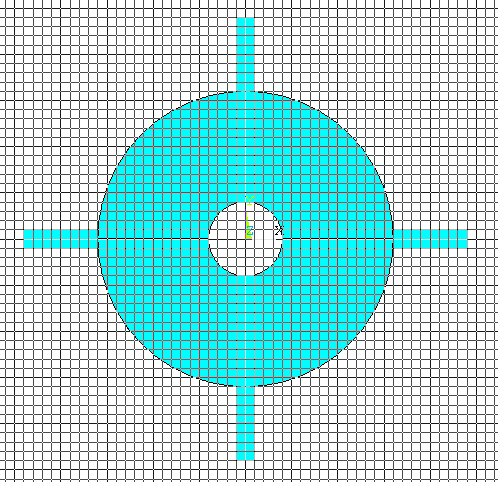
 |
Now we will add the
areas up. Go to
Preprocessor>Modeling>Operate>Booleans>Add>Areas.
|
 |
In the window that
comes up click "Pick all".
|
MATERIAL PROPERTIES:
 |
Go to the ANSYS
Main Menu |
 |
Click
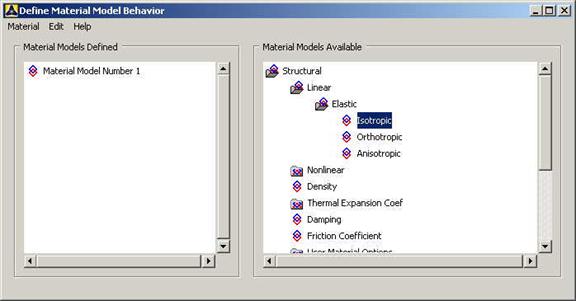
Preprocessor>Material Props>Material Models.
In the window that comes up, select
Structural>Linear>Elastic>Isotropic.
|
 |
Enter 1 for the
Material Property Number and click OK. The following window comes up.
|
 |
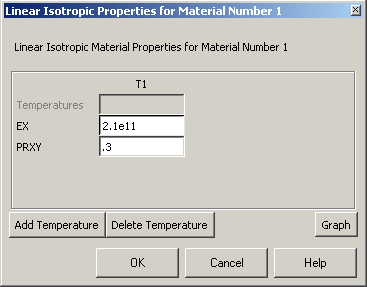
Fill in 2.1e11
for the Young's modulus and 0.3 for minor Poisson's Ratio.
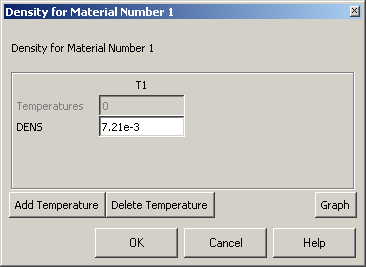
From the Material Model window, select
Structural>Density
and enter
7.21e3 for the density. Click OK. |
 |
Now the material 1
has the properties defined in the above table. We will use this
material for the structure. |
ELEMENT PROPERTIES:
 |
SELECTING ELEMENT
TYPE: |
 |
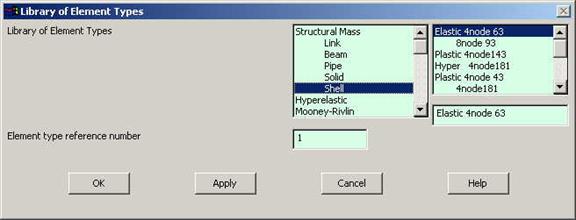
Click
Preprocessor>Element Type>Add/Edit/Delete...
In the 'Element Types' window that opens click on Add... The following
window opens: |
 |
Type 1 in
the Element type reference number. |
 |
Click on
Structural Shell and select Elastic 4node 63. Click OK.
Close the 'Element types' window. |
 |
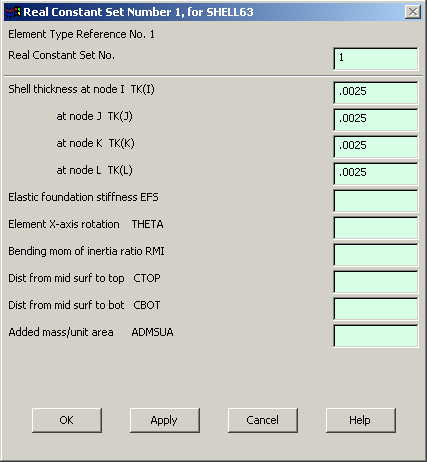
Now we need to
define the thickness for this element. |
 |
Go to
Preprocessor>Real Constants>Add/Edit/Delete...
|
 |
In the "Real
Constants" dialog box that comes up click on Add |
 |
In the "Element
Type for Real Constants" that comes up click OK. The following window
comes up. |
 |
Fill in the
relevant values and click on OK. |
 |
We have now defined
the thickness of the element. |
MESHING:
 |
Go to
Preprocessor>Meshing>Size Controls>Manual Size>Lines>Picked Lines.
Pick all the lines on the outer boundary of the figure and click OK.
|
 |
In the menu that
comes up type 0.025 in the field for 'Element edge length'.
|
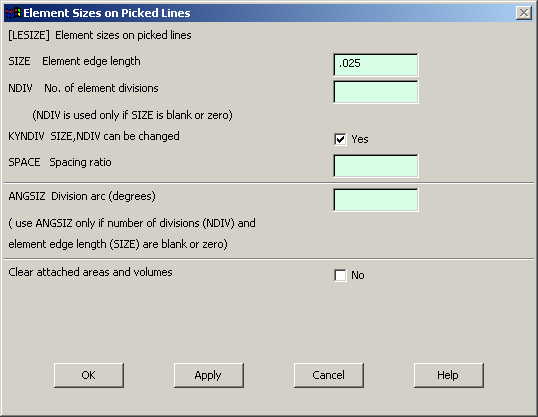
 |
Click on OK.
|
 |
Now go to
Preprocessor>Meshing>Mesh>Areas>Free.
|
 |
Click "pick all" in
the "Mesh Areas" dialog box. The meshed model looks like this.
|
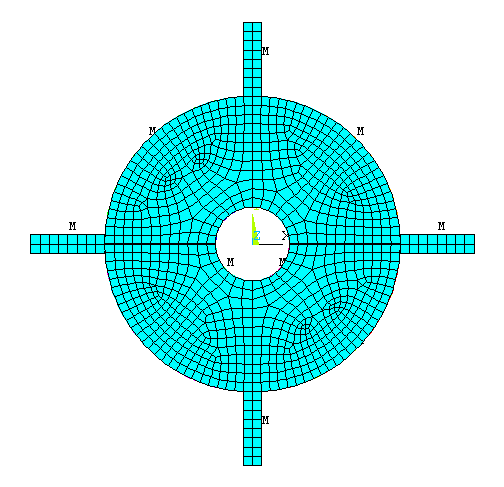
 |
Now the
blisk is divided into Shell elements.
|
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS AND
CONSTRAINTS:
 |
APPLYING BOUNDARY
CONDITIONS |
 |
The
blisk is fixed around the inner diameter
of the disk. |
 |
Go to Main Menu
Preprocessor>Loads>Define Loads>Apply>Structural>Displacement>On Lines.
|
 |
Select the lines on
the inner circumference of the disk and click OK. The following window
comes up: |
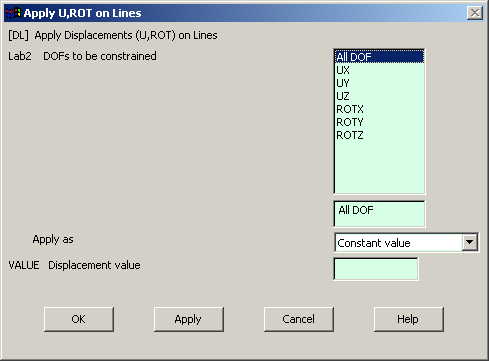
 |
Select All DOF
and click OK. |
 |
The model now looks
like this: |
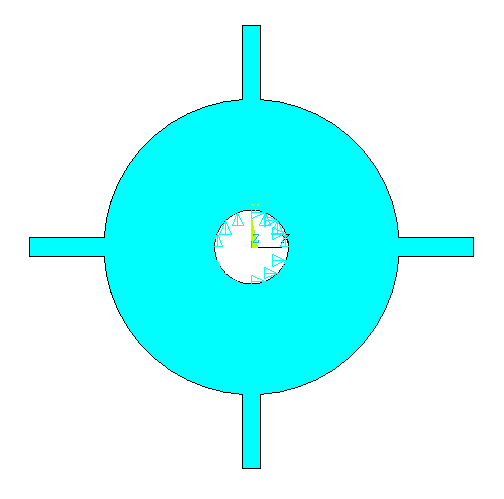
 |
Now the Modeling of
the problem is done. |
SOLUTION:
 |
Go to ANSYS
Main Menu>Solution>Analysis Type>New Analysis.
The following window comes up: |
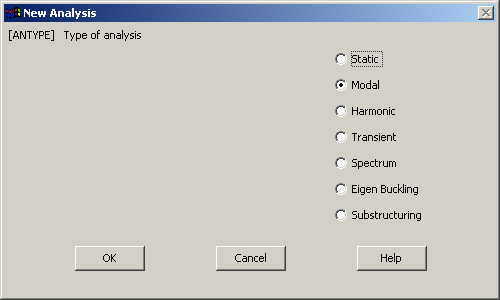
 |
Select Modal and
click on OK. |
 |
Now go to
Main Menu>Solution>Analysis Type>Analysis Options.
The following window comes up: |

 |
Enter the values
shown in the window above and click OK. The following window comes up.
|
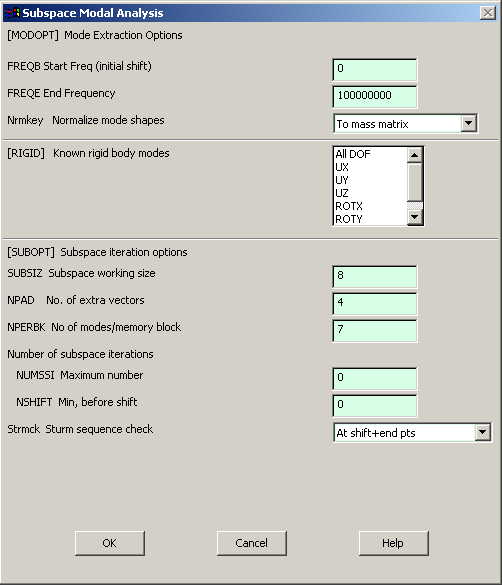
 |
Enter 100000000
for the End Frequency. Then Click OK. |
 |
Go to
Solution>Solve>Current LS.
|
 |
Wait for ANSYS to
solve the problem. |
 |
Click on OK and
close the 'Information' window. |
POST-PROCESSING:
 |
To list the first
three frequencies, go to
Main
Menu>General Postprocessing>Results
Summary.
The following window will be displayed: |

 |
To animate the mode
shapes, go to
Main
Menu>General Postprocessing>Read
Results>First Set.
|
 |
Go to
Utility Menu>Plot Controls>Animate>Mode Shape.
The following window will come up: |

 |
Select the required
animation: in this case Deformed Shape and click OK.
|
 |
The animation will
be similar to the ones below. (Don't capture images from these files,
they are not the solutions. Just similar to solutions.)
|
MODIFICATIONS:
 |
To plot the
deformed shape, go to
Main
Menu>General Postprocessing>Read
Results>First Set.
|
 |
Now in the same
window go to
Plot
Results>Contour Plot>Nodal Solution.
The following window comes up: |

 |
Select DOF
solution, and select USUM. |
 |
Check the Def +
undeformed button. |
 |
Click on OK. The
contour plot will look similar to the figure below. |