| |
GH Example |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
<Curve>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> |
|
|
| |
Transformaiton |
|
|
| |
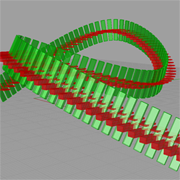 |
Description:
Transformation is commonly used as modling or manipulating the geometry objects in the Cartesian coordinate system. The exercise is meant to demonstrate how tranformation can be used to create a series of Box objects along a given curve. |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
Polar Curve |
|
|
| |
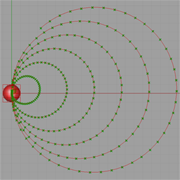 |
Description:
Polar/sphere system is useful as manipulating geometry on spherical space. This exercise we try to use the "Polar point" component to create periodic curve object. |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
Hypocycloid |
|
|
| |
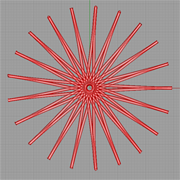 |
Description:
A Hypocycloid is a special plane curve generated by the trace of a fixed point on a small circle that rolls within a larger circle. In this example, we demonstarte how Expression components can be used to derive functional shapes. |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
Epicycloid |
|
|
| |
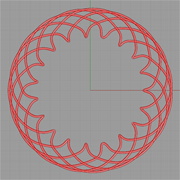 |
Description:
Similar to a Hypocycloid, an Epicycloid is also a plane curve produced by tracing the path of a chosen point of a circle — called epicycle — which rolls without slipping around a fixed circle. It is a particular kind of roulette. This is one equation-driven modeling example. |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
<Logic>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> |
|
|
| |
Cube Randomizations |
|
|
| |
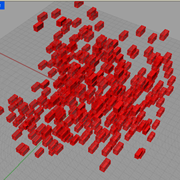 |
Description:
This Example shows the usage of two set of LOGIC components, List and Sets, coupled with the XForm transformation components. |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
City Blocks |
|
|
| |
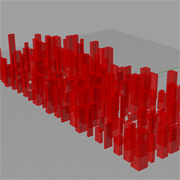 |
Description:
This example introduces the graph component to manipulate the position of cubes to have a random-like distribution.
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
List Manipulation |
|
|
| |
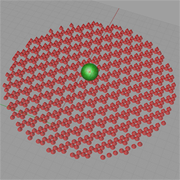 |
Description:
To better understand the logistics of operating a data list, This example incoporate several Logic components, such as List(Sort, SubList, Split List) and Sets (Range) to illustrate the manipulation of list elements. |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
<Surface>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> |
|
|
| |
Mobius Strip |
|
|
| |
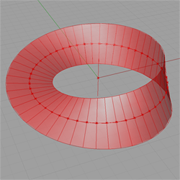 |
Description:
This example demonstrates how to use transfomration components to derive a mathematical surface, MöbiusStrip. The steps involve:
(1) Translate the line segments along the base circle and (2) rotate each line segment incrementally, and the total rotational range should be a multiple of pi. |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
ExtrudeSurface |
|
|
| |
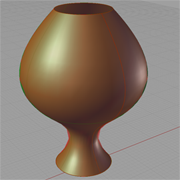 |
Description:
Three tranditional surface constructions are demonstarted in this example. They are extrude surface, transational surface and rotational surface. |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
Follow Points on Surface |
|
|
| |
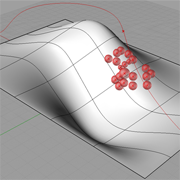 |
Description:
Another example shows how to use external resources, points along the selected curve in trhis case, as the input to control the sphere generated along the surface. |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
Surface Normal |
|
|
| |
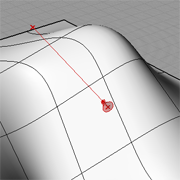 |
Description:
This example demonstrates how to use Surface Analysis components to derive the surface normal properties. These untities are useful and rewuired when further surface manipulations are planned. |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
Cull Patterns on Surface |
|
|
| |
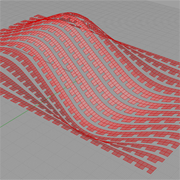 |
Description:
Similar to FuntionalPattern, this example illustartes another way to control the pattern generations on surface. A list of boolean values is used for the sub surface pattern generations. |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
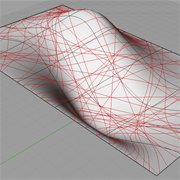
Random Intersections |
|
|
| |
 |
Description:
The pattern is generated by randomly created intersecting planes and then uses the intersecting component to derive surface curves.
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
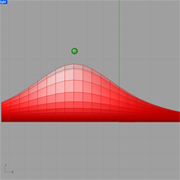
openSurface |
|
|
| |
 |
Description:
The example shows how to integrate external resources to create surface components.
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
Responsive Component |
|
|
| |
 |
Description:
Similar to openSurface example, this one takes other approaches to create responsive surface components.
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|